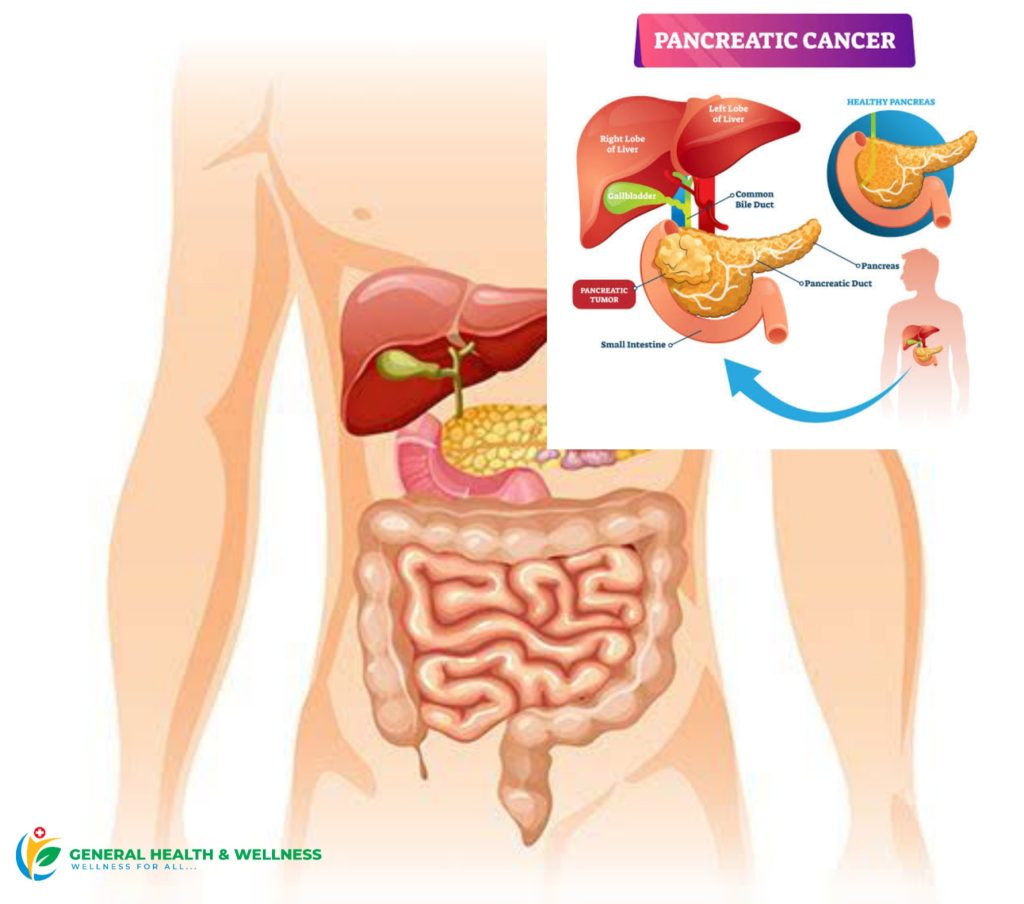
Pancreatic cancer is a serious disease that begins in the tissues of the pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach that plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation.
Because it often shows no symptoms in the early stages, pancreatic cancer is frequently diagnosed late, making awareness and early detection critical.
What is Pancreatic Cancer?
Pancreatic cancer develops when abnormal cells in the pancreas grow uncontrollably and form a tumor. It is one of the more aggressive cancers, often spreading rapidly to nearby organs.
Pancreatic Cancer Vaccine
Recent research has led to experimental pancreatic cancer vaccines designed to train the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
- These vaccines are not yet widely available but have shown promise in clinical trials.
- They are typically used alongside other treatments, such as chemotherapy, to improve survival chances.
(Source: National Cancer Institute)
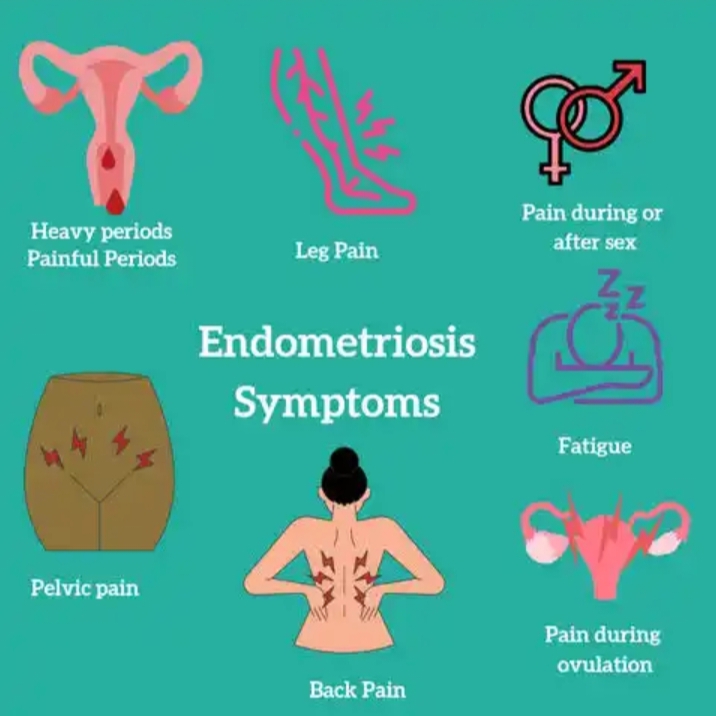
Endometriosis Pain and Periods: Symptoms and Solutions
Symptoms of Pancreatic Cancer
Early stages may be symptom-free, but possible signs include:
- Persistent abdominal or back pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Light-colored stools or dark urine
If you experience any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, seek medical evaluation promptly.
Pancreatic Cancer Survival Rates
Survival depends on the stage at diagnosis:
- Localized cancer: Higher survival rate if treated early.
- Advanced cancer: Lower survival rate, but targeted therapies and clinical trials offer new hope.
According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for localized pancreatic cancer is about 44%, while the overall rate across all stages is about 12%.
Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
Treatment plans depend on cancer stage, health status, and patient preference:
- Surgery – Removal of the tumor (Whipple procedure is most common).
- Chemotherapy – Drugs to destroy cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy – High-energy beams to shrink or kill cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy – Drugs that specifically attack cancer cell mechanisms.
- Immunotherapy – Stimulates the immune system to fight cancer.
Simple Action Plan
- Get regular check-ups if you have a family history of pancreatic cancer.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol.
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly.
- Ask your doctor about genetic testing if pancreatic cancer runs in your family.
Quick Facts about Pancreatic Cancer
- Pancreatic cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the U.S.
- Risk factors include smoking, obesity, diabetes, chronic pancreatitis, and genetic syndromes.
- Early detection greatly improves treatment outcomes.